Installation
Copy
# Install the Athina Logger SDK, Langchain and Langchain OpenAI
pip install athina-logger langchain langchain_openai --upgrade
Copy
# Set the Athina API Key for logging the traces to Athina
from athina_logger.api_key import AthinaApiKey
AthinaApiKey.set_api_key(os.getenv('ATHINA_API_KEY'))
LangchainCallbackHandler to create a trace for every run of your Langchain application.
Copy
# Import the LangchainCallbackHandler
from athina_logger.tracing.callback.langchain import LangchainCallbackHandler
athina_handler = LangchainCallbackHandler()
# Add the handler as callback to the invoke method of the chain
# chain.invoke({"input": "<user_input>"}, config={"callbacks": [athina_handler]})
Getting Started
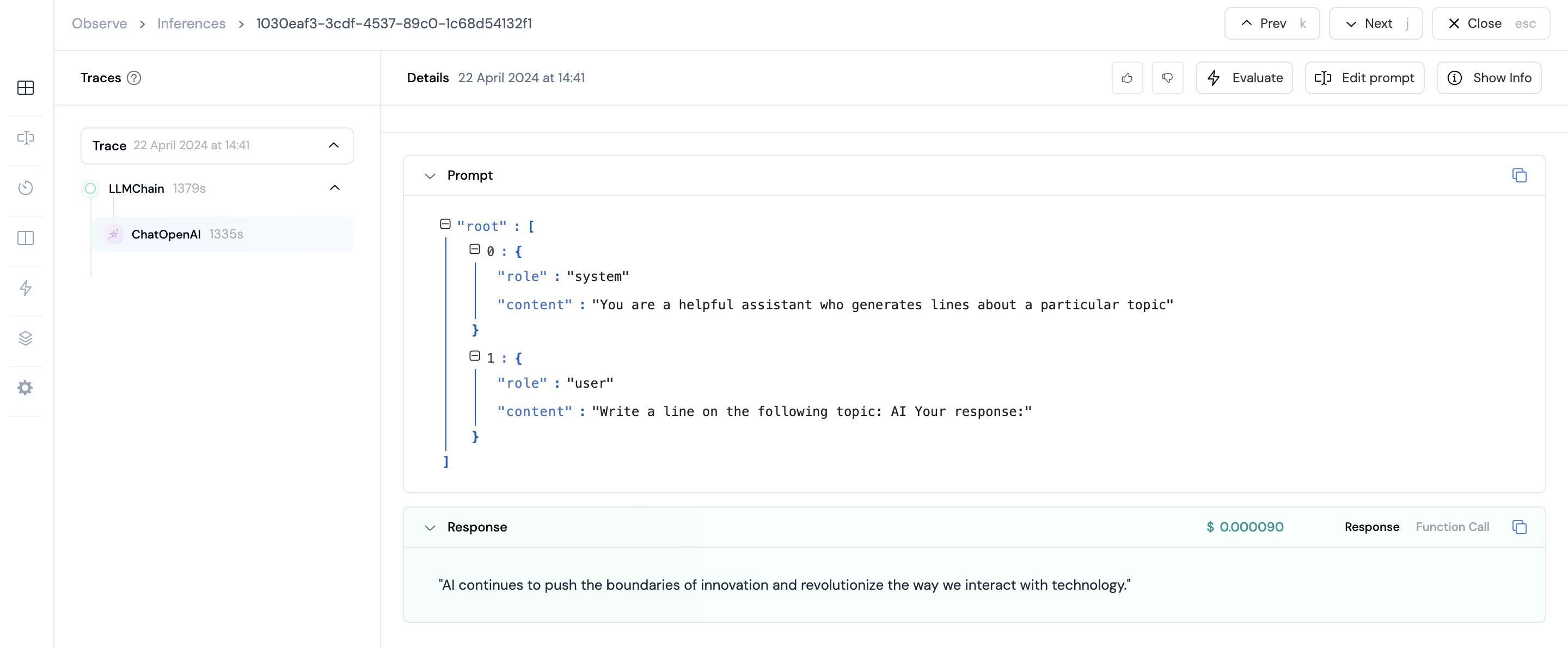
Following is an example of how to use the tracing library in your langchain application.Copy
# Import the necessary libraries
from langchain.chains.llm import LLMChain
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts.chat import (
ChatPromptTemplate,
SystemMessagePromptTemplate,
HumanMessagePromptTemplate,
)
# Import the LangchainCallbackHandler from the athina logging library
from athina_logger.tracing.callback.langchain import LangchainCallbackHandler
from athina_logger.api_key import AthinaApiKey
import os
# Set the Athina API Key for logging the traces to Athina
AthinaApiKey.set_api_key(os.getenv('ATHINA_API_KEY'))
# Create a prompt template for the chat
system_template = '''You are a helpful assistant who generates lines about a particular topic'''
system_message_prompt = SystemMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(system_template)
template = '''Write a line on the following topic: {text} Your response:'''
chat_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([system_message_prompt, HumanMessagePromptTemplate.from_template(template)])
# Create a chain and add the LangchainCallbackHandler as a callback
chain1 = LLMChain(
llm=ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key= os.getenv('OPENAI_API_KEY')),
prompt=chat_prompt,
)
response = chain1.invoke('AI', {"callbacks":[LangchainCallbackHandler()]})
print("Response:", response)
# The response will be printed in the console and the trace will be available in the Athina UI
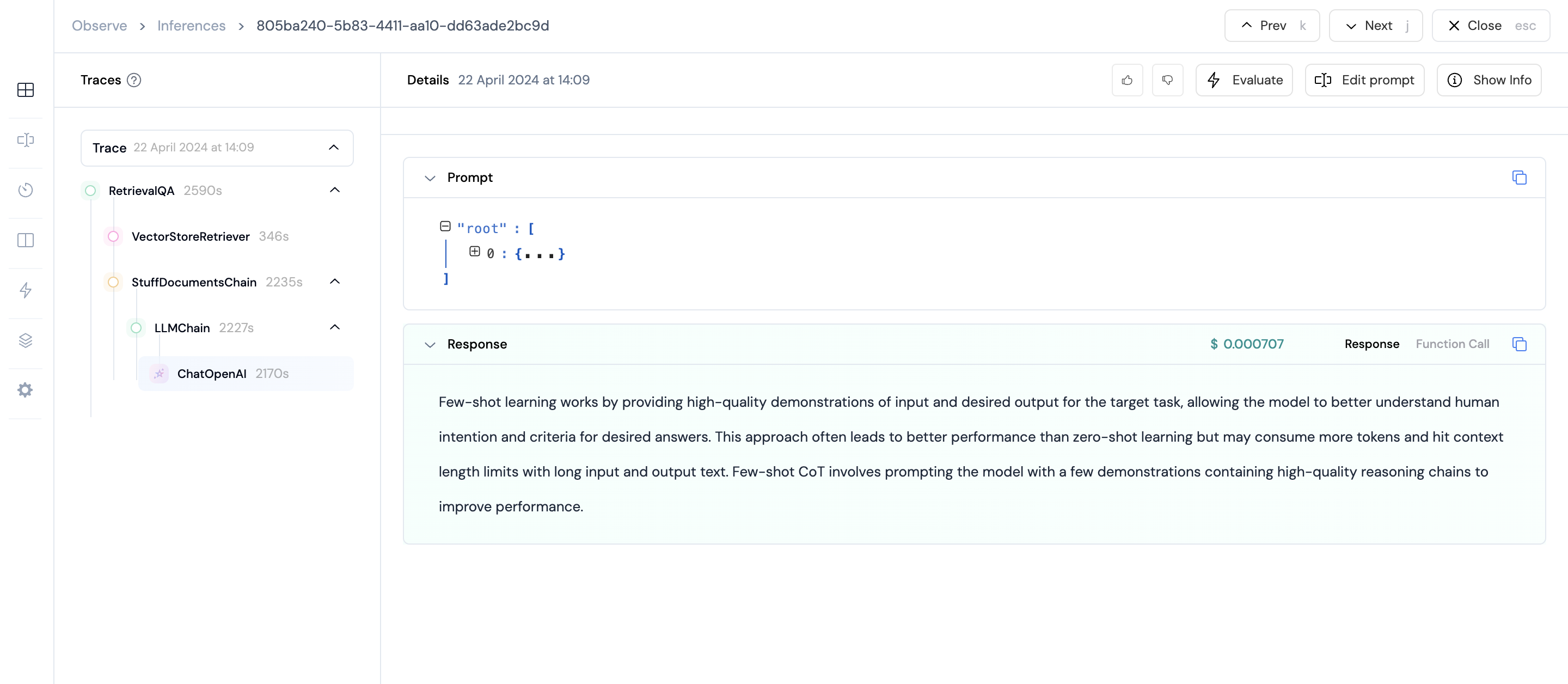
Retrieval QA Example
Copy
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.embeddings import OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_community.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import RetrievalQA
from langchain import hub
from athina_logger.api_key import AthinaApiKey
from athina_logger.tracing.callback.langchain import LangchainCallbackHandler
AthinaApiKey.set_api_key(os.getenv("ATHINA_API_KEY"))
# Load
loader = WebBaseLoader(
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/"
)
data = loader.load()
# Split
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=0)
all_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(data)
# Store splits
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=all_splits, embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings())
# LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# Prompt
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt", api_url="https://api.hub.langchain.com")
# RetrievalQA
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_llm(
llm, retriever=vectorstore.as_retriever(), prompt=prompt
)
# Query
question = "How does few shot learning work?"
# Invoke
result = qa_chain.invoke(
{"query": question}, {"callbacks": [LangchainCallbackHandler()]}
)
# Print result
print(result["result"])
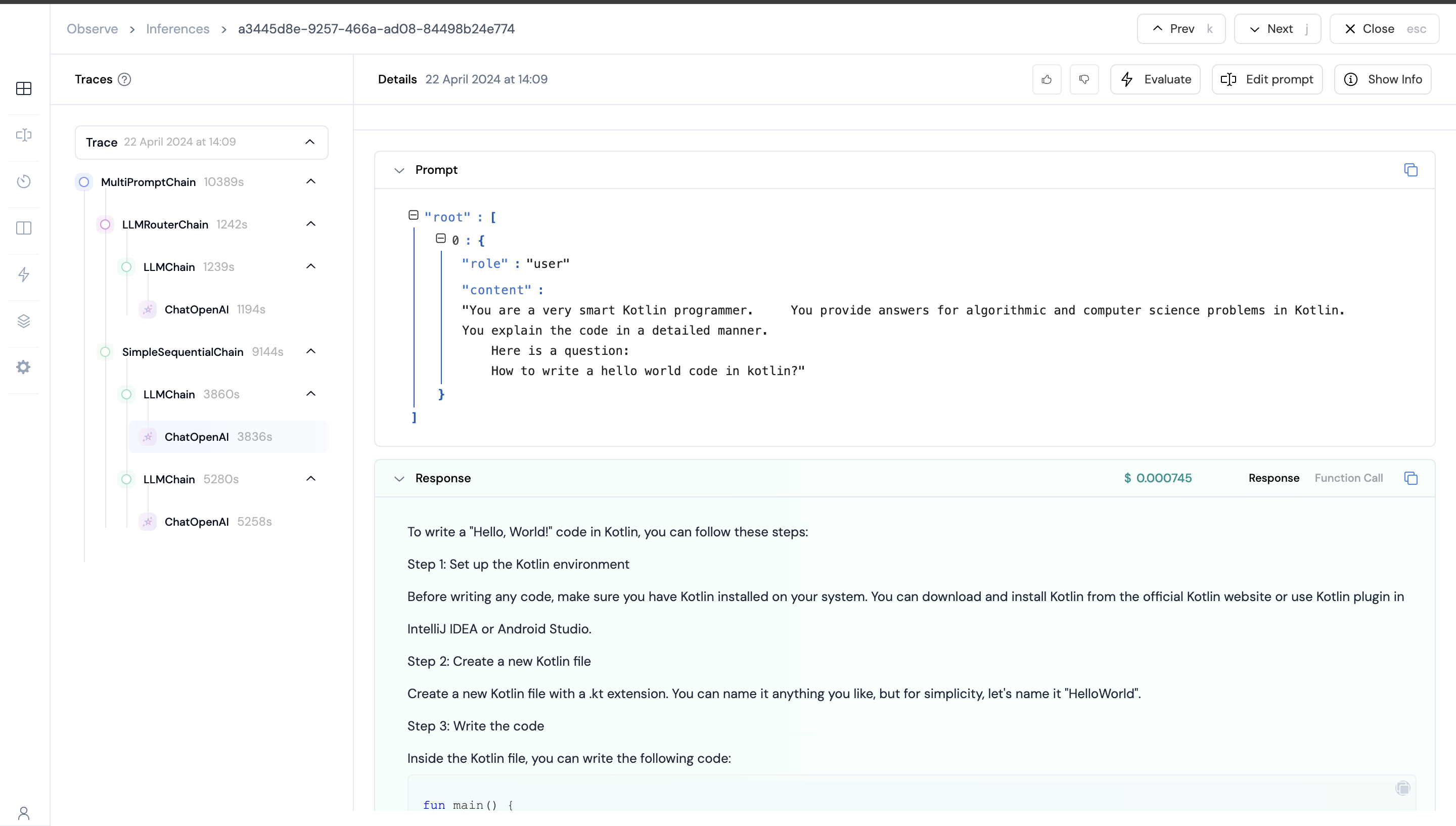
Complex example with multiple chains
Copy
from langchain.chains.router import MultiRouteChain, RouterChain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.chains.llm import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains.router.llm_router import LLMRouterChain, RouterOutputParser
from langchain.chains.router.multi_prompt_prompt import MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE
from langchain.chains import SimpleSequentialChain
from typing import Mapping, List, Union
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
from athina_logger.api_key import AthinaApiKey
from athina_logger.tracing.callback.langchain import LangchainCallbackHandler
AthinaApiKey.set_api_key(os.getenv("ATHINA_API_KEY"))
class Config():
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo-0613'
llm = ChatOpenAI(model=model, temperature=0)
cfg = Config()
class PromptFactory():
developer_template = """You are a very smart Python programmer. \
You provide answers for algorithmic and computer problems in Python. \
You explain the code in a detailed manner. \
Here is a question:
{input}"""
python_test_developer_template = """You are a very smart Python programmer who writes unit tests using pytest. \
You provide test functions written in pytest with asserts. \
You explain the code in a detailed manner. \
Here is a input on which you create a test:
{input}"""
kotlin_developer_template = """You are a very smart Kotlin programmer. \
You provide answers for algorithmic and computer science problems in Kotlin. \
You explain the code in a detailed manner. \
Here is a question:
{input}"""
kotlin_test_developer_template = """You are a very smart Kotlin programmer who writes unit tests using JUnit 5. \
You provide test functions written in JUnit 5 with JUnit asserts. \
You explain the code in a detailed manner. \
Here is a input on which you create a test:
{input}"""
python_programmer = 'python programmer'
kotlin_programmer = 'kotlin programmer'
programmer_test_dict = {
python_programmer: python_test_developer_template,
kotlin_programmer: kotlin_test_developer_template
}
prompt_infos = [
{
'name': python_programmer,
'description': 'Good for questions about coding and algorithms in Python',
'prompt_template': developer_template
},
{
'name': 'python tester',
'description': 'Good for for generating Python tests from existing Python code',
'prompt_template': python_test_developer_template
},
{
'name': kotlin_programmer,
'description': 'Good for questions about coding and algorithms in Kotlin',
'prompt_template': kotlin_developer_template
},
{
'name': 'kotlin tester',
'description': 'Good for for generating Kotlin tests from existing Kotlin code',
'prompt_template': kotlin_test_developer_template
}
]
class MultiPromptChain(MultiRouteChain):
"""A multi-route chain that uses an LLM router chain to choose amongst prompts."""
router_chain: RouterChain
"""Chain for deciding a destination chain and the input to it."""
destination_chains: Mapping[str, Union[LLMChain, SimpleSequentialChain]]
"""Map of name to candidate chains that inputs can be routed to."""
default_chain: LLMChain
"""Default chain to use when router doesn't map input to one of the destinations."""
@property
def output_keys(self) -> List[str]:
return ["text"]
def generate_destination_chains():
"""
Creates a list of LLM chains with different prompt templates.
Note that some of the chains are sequential chains which are supposed to generate unit tests.
"""
prompt_factory = PromptFactory()
destination_chains = {}
for p_info in prompt_factory.prompt_infos:
name = p_info['name']
prompt_template = p_info['prompt_template']
chain = LLMChain(
llm=cfg.llm,
prompt=PromptTemplate(template=prompt_template, input_variables=['input']),
output_key='text'
)
if name not in prompt_factory.programmer_test_dict.keys():
destination_chains[name] = chain
else:
# Normal chain is used to generate code
# Additional chain to generate unit tests
template = prompt_factory.programmer_test_dict[name]
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(input_variables=["input"], template=template)
test_chain = LLMChain(llm=cfg.llm, prompt=prompt_template, output_key='text')
destination_chains[name] = SimpleSequentialChain(
chains=[chain, test_chain], verbose=True, output_key='text'
)
default_chain = ConversationChain(llm=cfg.llm, output_key="text")
return prompt_factory.prompt_infos, destination_chains, default_chain
def generate_router_chain(prompt_infos, destination_chains, default_chain):
"""
Generats the router chains from the prompt infos.
:param prompt_infos The prompt informations generated above.
:param destination_chains The LLM chains with different prompt templates
:param default_chain A default chain
"""
destinations = [f"{p['name']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
destinations_str = '\n'.join(destinations)
router_template = MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE.format(destinations=destinations_str)
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=['input'],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser()
)
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(cfg.llm, router_prompt)
multi_route_chain = MultiPromptChain(
router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=destination_chains,
default_chain=default_chain,
verbose=True,
)
return multi_route_chain
if __name__ == "__main__":
prompt_infos, destination_chains, default_chain = generate_destination_chains()
chain = generate_router_chain(prompt_infos, destination_chains, default_chain)
question = "How write a hello world code in kotlin?"
result = chain.invoke(question, {"callbacks":[LangchainCallbackHandler()]})
print(result)